What is stress-strain diagram?
Dear learners,
Here are fruitful informations about stress-strain diagram!!
According to Hooke’s experiment, the reaction between the stress & strain for a specimen under tensile stress can be found experimentally.
If we draw a plot(graph) of stress $(\sigma)$ vs strain $(\epsilon)$ for any metal body, we can see an ideal curve as shown below.
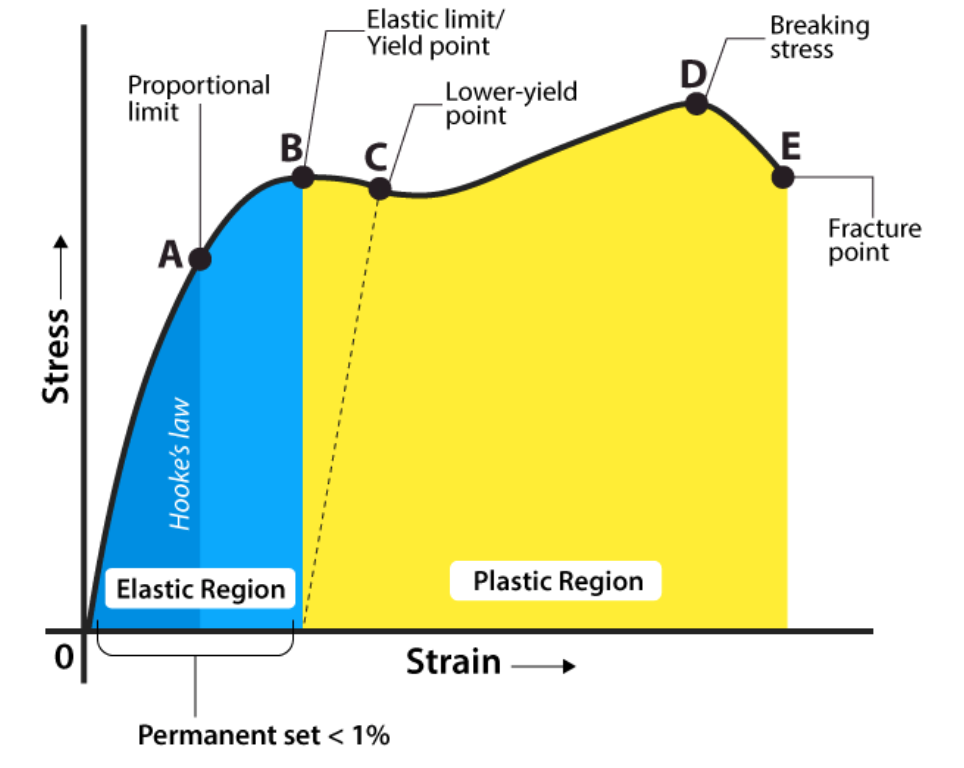
This shows that as stress increases strain on the material will also increase, but after certain point the curve becomes non-uniform and (i.e., between point A & E).
Thus the region between A to B stress and strain are not proportional to each other (Hooke’s law is not valid in this zone). The point B in the curve is known as yield point (also known as elastic limit) and the corresponding stress is known as yield strength $(\sigma_y)$ of the material. Below this point the body can retain its original shape and size but if yield stress goes beyond $(\sigma_y)$ the body will start deforming and it is said to be permanently deformation.
From Hooke’s law:
$\sigma \propto \epsilon$
$\sigma =E \epsilon$
Where, $E$ is proportionality constant which is known as Young’s modulus of elasticity. It is also determined by calculating slope of stress vs strain curve.
Young’s modulus of elasticity $(E)$: It is the ratio of Longitudinal stress $(\sigma)$ to the longitudinal strain $(\epsilon)$ is defined as Young’s modulus.
$E=\frac{\text{Longitudinal stress} (\sigma)}{\text{Longitudinal strain} (\epsilon)}=\frac{\frac{F}{A}}{\frac{\Delta L}{L}}$
Where,
$F=$ force applied
$A=$ area of cross section
$\Delta L =$ change in length
$L=$ original length
Some useful definitions:
- Proportional limit: in this region, stress is proportional to strain. i.e. Region in which the curve follows Hooke’s law.
- Yield point: The point on a stress-strain curve indicates the limit of elastic behaviour and the beginning of plastic behaviour.
- Ultimate strength (UTS) or Breaking stress: The point after which material will break. The point at which the material endures maximum stress before failure is known as UTS. From this point, necking start formation.
If flow stress equation is given as:
$\sigma= k\epsilon^n$
Then at UTS: (Very important for GATE Exam)
$\epsilon=n $
- Fracture point: The point at which the material breaks.